If you’ve ever sent or received money internationally, chances are that you’re wondering what a SWIFT transfer is all about.
Over 11,500 financial institutions across 200+ countries rely on the SWIFT network. Hence, making it the backbone of global payment transactions.
In this guide, we’ll be exploring what a SWIFT transfer is, the best ways to use it, and tips to help you gain the best advantage.
Table of Contents
What is a SWIFT Transfer?
To deeply understand what a SWIFT transfer is, let’s start off by defining its abbreviation.
SWIFT stands for the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications.
However, it isn’t a bank or a payment processor. Instead, SWIFT transfer is a secure messaging network that allows banks and financial institutions to send standardised instructions for cross-border payments.
It also refers to a SWIFT Code (or Bank Identifier Code – BIC), an international bank code of 8 or 11 characters that identifies a specific bank and its location for these transfers.
In simple terms, SWIFT is the postal service for financial messages. It doesn’t transfer the money itself, but it delivers the instructions to the right destination.
SWIFT Technology Evolution
SWIFT has been evolving with initiatives like SWIFT GPI (Global Payments Innovation), launched in 2017, to speed up payment tracking and processing transparency.
SWIFT GPI enables same-day or next-day payments with real-time tracking, addressing some traditional SWIFT delays. However, fees and intermediary banks remain considerations.
How Does a SWIFT Transfer Work?
Understanding what a SWIFT transfer is becomes easier when you know how the process works from start to finish.
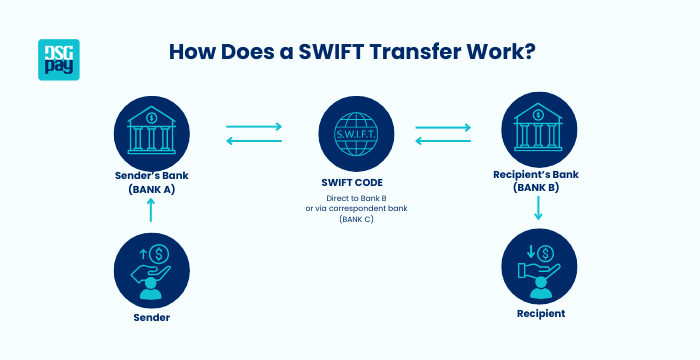
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of what happens during a SWIFT transfer.
- Initiation: This is when you want to send money to an overseas account, so you request an international transfer at your bank.
- Message Sent: Your bank creates a SWIFT message that contains the payment details you filled in. This is the amount to send, the currency you’re converting to, the destination account details, etc.
- Routing: If there’s no direct relationship between your bank and the recipient’s bank, intermediary or correspondent banks are used.
- Processing: The recipient bank receives the message, verifies it, and deposits the funds into the destination account you’ve filled in.
- Completion: The beneficiary receives the money, usually after 1-5 business days, depending on the banks and countries involved.
Cost and Speed of SWIFT Transfers in 2026
Cost of SWIFT Transfers
SWIFT transfers are secure but often come with multiple fees from different parties, including:
- Outgoing Transfer Fees: This fee is charged by your bank and typically ranges from $10 to $50.
- Intermediary Bank Fees: Each correspondent bank can deduct fees, usually in the range of $10-$30.
- Incoming Fees: The recipient’s bank may also charge fees for receiving the money, around $5-$20.
- Exchange Rate Markups: Banks often apply a margin – about 1-3% above the mid-market exchange rate.
Because of these fees, if you send $1000 via SWIFT, the recipient will likely receive around $940 to $970 after deductions.
Speed of SWIFT Transfers
The time stream for a SWIFT transfer usually includes the following times:
- Standard Processing: A normal SWIFT transfer usually takes 2-5 business days.
- Delays: Public holidays, multiple intermediary banks, or compliance checks can slow down the process.
- Same-Day Payments: Possible in some cases (e.g., within Europe or the same banking group), but less common internationally.
Note: Fees and processing times vary widely depending on the counties and banks involved. Transfers involving emerging markets or less-connected banking corridors often incur higher intermediary fees or longer delays.
Advantages and Limitations of Using SWIFT Transfers
Advantages of Using SWIFT Transfers
Below are some of the reasons why SWIFT has become renowned since it started operations in 1977.
- Global Reach: The SWIFT network connects over 11,000 financial institutions across more than 200 countries and territories, enabling transfers to almost any location worldwide.
- Enhanced Security: SWIFT uses strong encryption, authentication protocols, and a standardised messaging system to protect sensitive financial data and prevent fraud and cyber threats.
- Standardised Messaging: The use of standardised message formats (like ISO 20022) ensures clear, consistent, and error-free communication between banks, reducing miscommunication and facilitating automated processing.
- Transparency and Traceability: SWIFT transfers include a unique reference number and time stamp that allows both the sending and receiving banks to track the payment’s progress in real time.
- Regulatory Compliance: The SWIFT system complies with international financial laws, including the anti-money laundering (AML) and sanction screening laws, which help financial institutions in risk assessment and management and transaction documentation.
- Versatility: The SWIFT network supports a wide range of financial transactions beyond simple payments, including securities trading and foreign exchange.
Limitations of SWIFT Transfers
Below are the limitations of the SWIFT network when compared with other payment methods available in 2026.
- High Costs of Transfers: Marked-up exchange rates and multiple fees from the sending, intermediary, and receiving banks increase the overall cost of SWIFT transfers.
- Expensive for Small Transfers: Due to fixed and high-percentage-based fees, SWIFT transfers can be disproportionately expensive for small transactions.
- Slow Processing Time: Standard SWIFT transfers can take 2 to 5 business days to complete. The involvement of multiple intermediary banks makes the process long.
- Precise Recipient Information Requirements: Users need to provide a lot of detailed information, including the recipient’s full name, address, bank account number, and the correct SWIFT/BIC code.
- Complex Fee Structure: Due to the involvement of several banks and unknown intermediary fees, it can be difficult to know the total cost of a SWIFT transfer upfront.
- Possibility of Delays or Rejections: Incorrect payment details, such as the wrong SWIFT code or a missing recipient address, can lead to delays or outright rejection of the transfer. Delays and rejections can also occur due to national holidays, different time zones, or technical difficulties with the system.
When Should You Use SWIFT Transfers?
Now that you know the answer to what SWIFT transfer is and how it works, you can consider the best times to use the SWIFT network for your cross-border transactions.
SWIFT is most suitable for when:
- You prefer working directly with traditional banks.
- You are making large business-to-business (B2B) payments that require security and traceability.
- You need to send money to a country or currency not covered by local systems (like SEPA in Europe).
- Your recipient is in a region where fintech or alternative payment solutions aren’t widely adopted.
The SWIFT network can also be used for a wide range of other international transactions, provided the cost and processing time meet your needs.
Alternatives to SWIFT Transfers in 2026
With the rise of fintech and digital platforms, alternatives to SWIFT are becoming increasingly popular. Some of them are:
1. SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area)
The SEPA is a European initiative that allows fast and low-cost transfers in euros across the Eurozone. SWIFT was created in 1973 and started operations in 1977; following that, SEPA was created in 2008 to streamline euro payments.
SEPA payments are designed to be fast, low-cost, and transparent but only apply to transactions in EUR between EU and EEA member states. While SEPA is highly efficient within Europe, it does not provide the same global coverage as SWIFT.
- Speed: Usually same-day or next-day transfers.
- Cost: Often free or under €1 if the transaction is within the Eurozone.
- Best For: Businesses and individuals making cross-border euro payments within Europe.
2. Online Money Transfer Services
Modern online money transfer services use fintech innovations to make international transfers faster and more affordable. Examples include Wise, Revolut, OFX, and DSGPay. They offer transparent fees, mid-market exchange rates, and user-friendly platforms.
- Speed: They usually complete transactions within 1-2 business days.
- Cost: They charge lower fees with transparent pricing and mid-market exchange rates.
- Best For: Freelancers, SMEs, and anyone making regular international transfers.
3. Cryptocurrency & Blockchain-Based Payments
Crypto blockchains facilitate cross-border peer-to-peer transfers without relying on traditional banking rails. Users can convert local currency into digital assets (such as stablecoins or cryptocurrencies) via exchanges like Binance or Coinbase, then transfer them globally. Some digital wallet apps like PayPal or Skrill also support crypto transactions.
- Speed: They usually complete transactions instantly or within hours.
- Cost: They charge lower fees than SWIFT, but the value of cryptocurrencies can be very volatile. Tax fees and limitations are also significant considerations for this alternative.
- Best For: Tech-savvy users who are into cryptocurrency trading.
Comparison of SWIFT and Its Alternatives in 2026
To know the best option for your needs, let’s compare each of the above methods to send money against one another.
| Feature | SWIFT Transfers | SEPA Transfers (Eurozone) | Online Money Transfer Services | Cryptocurrency |
| Coverage | 200+ countries, all major currencies | EU & EEA Countries, Euro-only | 70–170+ countries, multiple currencies | Global (depending on the blockchain) |
| Speed | 1–5 business days | Same day or next day | Instant to 2 days | Instant to hours |
| Cost | $20–$50+ plus hidden FX markups | Usually free or < €1 depending on the bank or currency | 0.5%–3% of transaction volume | Low (network fees only) |
| Transparency | Hidden fees in exchange rates | Standardised, minimal fees | Clear fees & mid-market rates | Secure but depends on the blockchain used |
| Best For | Large, global B2B payments | Euro payments within Europe | SMEs, freelancers, e-commerce, and frequent senders | Fast, borderless transfers for tech-savvy users |
SWIFT remains the most reliable option for large, global transactions, while SEPA, online transfer services, and blockchain-based payments each offer faster or cheaper alternatives depending on your needs
FAQs About SWIFT Transfers
Q. What are SWIFT transfers?
A SWIFT transfer is an international bank-to-bank payment made through the SWIFT messaging network.
Q. Are SWIFT transfers safe?
Yes, they are highly secure, as SWIFT uses encrypted financial messaging between banks.
Q. How much do SWIFT transfers cost?
Fees are different depending on the bank, but usually, SWIFT transfers fall in the range of $15 to $50 per transfer, plus exchange rate markups.
Q. Can I use SWIFT to send money to any country?
Yes, SWIFT connects more than 11,000 banks in over 200 countries worldwide.
Q. What is the difference between SWIFT and SEPA?
SWIFT is global, while SEPA is limited to Eurozone payments.
Q. When is SWIFT not the best option?
SWIFT transfers may not be ideal for small, urgent, or frequent transactions, since the fees are relatively high and processing times can take several business days. In such cases, local payment systems or online money transfer services may be more practical.
Q. Can DSGPay be used as an alternative to SWIFT transfers?
Yes, DSGPay offers faster and cost-effective cross-border payments, while still providing SWIFT transfers when required, making it a strong alternative for international businesses.
DSGPay: A Modern Alternative to SWIFT Transfers
For individuals and businesses that need a reliable and cost-effective way to move money across borders, DSGPay provides a strong alternative to traditional SWIFT transfers.
By leveraging local rails and virtual accounts, DSGPay makes international payments faster, more transparent, and more affordable.
Why Choose DSGPay
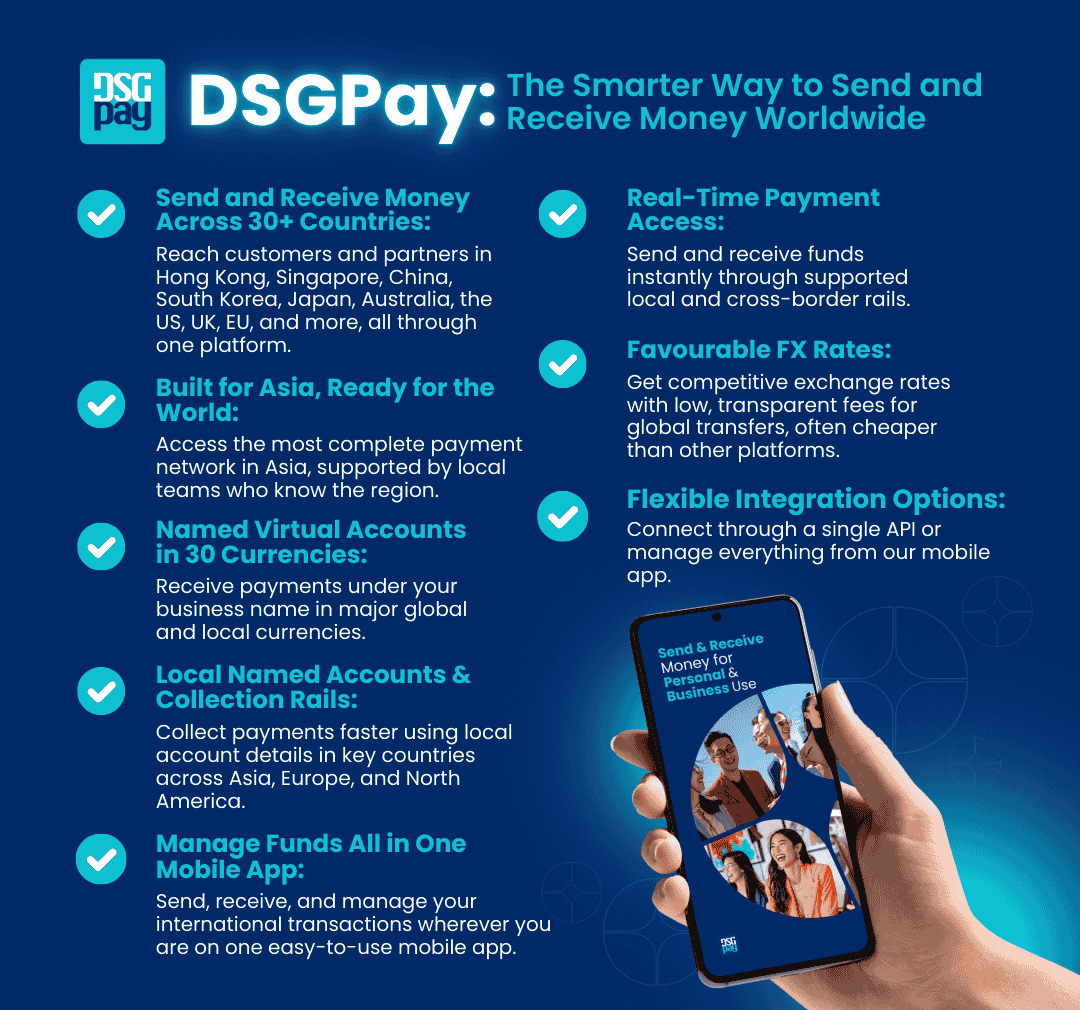
- Global and Local Named Virtual Accounts: You can open a global and local virtual account that carries your or your business name to send or receive payments from international clients with increased trust.
- Send and Receive Money Across 30+ Currencies: Access local collection accounts and payout options that make global business seamless.
- Competitive FX Rates and Low Fees: Get favourable exchange rates and lower transaction costs compared to traditional banks.
- Seamless API Integration: DSGPay’s API system is capable of connecting with online portals, e-commerce systems, and payout platforms like Upwork, Etsy, Amazon, and other online payment portals.
- Compliance & Dedicated Support: Operates under a Hong Kong MSO license, backed by strong AML standards and a dedicated account manager.
Final Thoughts
You should be familiar with what SWIFT transfers are all about with our guide. While it’s still an essential part of global finance, for individuals and businesses needing faster, cheaper, more versatile and flexible options, service platforms like DSGPay cover all the standards.
Be a part of the experience today!