When money moves across borders or between banks, it doesn’t travel on a highway; it moves through payment rails.
These rails are the background systems and networks that ensure payments get from sender to receiver safely, securely, and quickly.
Today, businesses and individuals rely on several different types of rails, and understanding them is the best way to know if you’re choosing the right method for your transaction.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Payment rails are the backbone of global money transfers. They are the underlying systems that move money between banks, businesses, and individuals globally.
- Businesses and individuals should choose payment rails based on cost, speed, and geographical reach.
- Multi-rail strategies are an option that streamlines cross-border payments by connecting users to the most efficient rails when making their transactions.
What Are Payment Rails?
Payment rails are the digital ways, or paths, that enable the movement of funds from one financial institution to another. You can think of them as the tracks or pathways that connect banks, money transfer services, online payment platforms, and other financial platforms together.
While most of the major systems today are electronic (like SWIFT and ACH), the term ‘payment rails’ broadly includes all methods from modern, instant networks to older, traditional mechanisms like paper cheques and bank wires.
Whether you make a direct deposit, pay a vendor, or send money internationally, your payment uses one or more of these rails to reach its intended destination.
These rails include multiple participants, starting from the sender, to the sender’s bank, to clearing and settlement systems (the rail itself), to the receiver’s bank, and finally, the receiver. By linking all these parties, payment rails ensure that each transaction is processed securely, complies with regulations, and reaches its destination on time.
How Do Payment Rails Work?
When a payment is made, several key steps occur on a payment rail. They are:
- Initiation: The sender (an individual or business) initiates the payment through their bank or payment provider.
- Authorisation: The sender’s financial institution verifies available funds in the account and then authorises the payment.
- Processing: Payment instructions travel over the payment rail to the recipient’s bank. Depending on the rail, this can happen in batches or in real time.
- Settlement: The sender’s and receiver’s banks adjust their account balances accordingly. Settlement can happen instantly or after a period of time.
- Confirmation: Both parties receive debit and credit notifications that the payment has been completed.
Tip: The speed, cost, and security of these steps vary widely depending on the payment rail used.
9 Common Types of Payment Rails in 2025
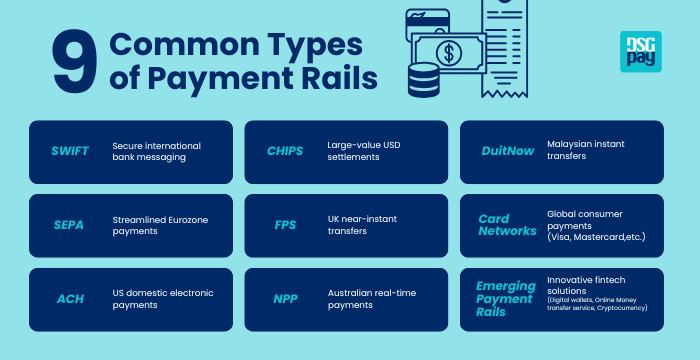
Here are some of the more common payment rails used in 2025:
1. SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication)
SWIFT is the global messaging network used by over 11,500 financial institutions in more than 200 countries. It is used to facilitate international bank-to-bank payment instructions. It does not move the money itself, but it securely transmits standardised instructions between banks for cross-border wire transfers and other financial messages.
While it is very secure, reliable, and globally accepted, the SWIFT rail is expensive, and it usually takes anywhere from 1 to 5 business days to complete a SWIFT transfer, depending on the receiver’s bank and its location unless you have access to SWIFT gpi, which is capable of minutes-to-same-day transactions.
Best For: This rail is best suited for large international transfers requiring compliance and traceability.
2. SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area)
SEPA is the Eurozone’s streamlined rail for euro-denominated payments across EU and EEA countries. It enables individuals and businesses to send and receive euro payments quickly with unified standards to foster cross-border transactions.
The SEPA rail covers 36 European countries, and transfers are generally free or very low-cost between them.
The SEPA rail includes three main services:
- SEPA Credit Transfer (SCT): Standard bank transfers, usually completed within one business day.
- SEPA Instant Credit Transfer (SCT Inst): Real-time payments available 24/7, settling within seconds for amounts up to €100,000.
- SEPA Direct Debit (SDD): For recurring payments like rent, subscriptions, or utility bills.
Best For: This rail is best used by individuals or businesses in Europe who are trading in euros.
3. ACH (Automated Clearing House)
ACH is a batch-processing and clearing payment rail that serves the United States. It is used for low-value, high-volume domestic electronic payments. This type of transaction includes payroll, vendor payments, and bill collections.
ACH money transfers usually charge very low fees, often under a dollar or a few cents per transaction, depending on the volume; however, they can only process payments in batches. This means payments can take anywhere from 1-3 business days before settlement, although most payments are same-day.
Best For: Domestic payments in the US. This includes direct deposit payrolls, automated bill payments, and vendor disbursements.
4. CHIPS (Clearing House Interbank Payment System)
CHIPS is the U.S. real-time gross settlement system, primarily used for large-value domestic and international wire payments. It handles billions of dollars daily, including many cross-border USD transactions.
CHIPS exclusively processes large-value USD transactions, making it more expensive than ACH. This is due to its handling of larger transactions, same-day settlement, and better risk controls.
Best For: International corporations, banks, and financial institutions dealing with large USD settlements.
5. FPS (Faster Payments Service)
FPS is one of the most widely used payment rails in the UK, providing near-instant domestic transfers in British pounds (GBP). Launched in 2008 by the UK Payments Council (now Pay.UK). FPS typically completes transfers within seconds, and the rail is accessible 24/7/365.
Most UK banks, fintech apps, and payment service providers are connected to FPS, making it the backbone of everyday digital payments in Britain. It costs low or no fees for individuals but offers competitive pricing for businesses.
Best For: Everyday P2P transfers, bill payments, and immediate interbank transactions or B2B transactions within the UK.
6. NPP (New Payments Platform)
The New Payments Platform (NPP), launched in 2018, is Australia’s real-time payment rail operated by NPP Australia under the Reserve Bank of Australia. It enables rapid, 24/7 domestic transfers, with settlement occurring in less than 60 seconds.
NPP uses overlay services like Osko by BPAYTM for fast peer-to-peer payments, PayTo for recurring payment authorisations, and PayID, which links user-friendly identifiers like mobile numbers, emails, or ABNs to a bank account. This removes the need to remember bank account numbers and other details.
Best For: Instant domestic AUD transfers for small businesses and everyday peer-to-peer payments within Australia, especially when using PayID for convenience.
7. DuitNow
DuitNow is Malaysia’s instant payment service built on the country’s Real-time Retail Payments Platforms (RPP). It allows instant transfers across banks and e-wallets and lets users link easy identifiers (emails, mobile numbers, or NRIC) instead of account numbers.
DuitNow supports QR code payments and is widely used for both personal and business transactions, as it is also a low-cost option.
Best For: Making peer-to-peer transfers, merchant payments, government disbursements, and bill payments with high convenience and speed.
8. Card Networks (Visa, Mastercard, etc.)
Card networks such as Visa, Mastercard, and other major cards operate powerful global payment rails connecting billions of consumers, merchants, and financial institutions worldwide. These networks have grown beyond just card-present (ATM) transactions to enable rapid, secure digital money movement across multiple use cases.
For example, some card network payment rails, such as Visa Direct or Mastercard Send, can complete transactions within 30 minutes and also facilitate instant refunds, gig economy payouts, peer-to-peer transfers, and cross-border remittances. However, some other card network rails, such as normal merchant settlements, still take days to complete transactions.
Card network rails are also capable of working in tandem with normal rail systems like SWIFT, ACH, or other instant payment rails, depending on the type of transaction, as they are globally accepted.
Best For: This payment rail is most suitable for consumer payments, online shopping, and gig economy payouts
9. Emerging Payment Rails
New rails powered by fintech innovations and technology, such as cryptocurrency blockchains, digital wallets, and API-driven online money transfer services, are reshaping the payment landscape.
These rails are often transparent, offer payment tracking, reduced costs, and improved interoperability, but they are not yet available in all parts of the world.
Best For: Users or businesses who are certain the receiver’s account has access to the same payment rail or network.

Comparison Table for the Common Payment Rails
The differences between each of the payment rails should assist you in picking the best rail(s) to use for your next international transaction.
| Payment Rail | Coverage | Currency Support | Speed | Cost | Security & Compliance |
| SWIFT | Global (200+ countries) | Any Currency | 1–5 business days (minutes with SWIFT gpi) | High (fees + FX markup) | Very high, regulated worldwide |
| SEPA | Eurozone (EU & EEA) | EUR only | Same day or next day | Low (free or minimal fee) | High, EU and EEA regulated |
| ACH | United States | Primarily USD | 1–3 business days | Low | US regulated |
| CHIPS | U.S. & cross-border USD settlements | Primarily USD | Same day | Moderate | Highly regulated |
| FPS | UK domestic only | GBP | Seconds | Low | Regulated UK payments |
| NPP | Australia | AUD | Seconds | Low | Australian financial regulations |
| DuitNow | Malaysia | MYR | Seconds | Low | Malaysian regulations |
| Card Payments | Global | Depends on the card issuer | Seconds – days | High | Card issuer regulations, global fraud standards |
| Emerging Rails | Varies (Global to Regional) | Depends on the network | Seconds to minutes | Low and competitive | Regulated by multiple international authorities |
After comparing the major payment rails side by side, it’s clear that each rail is designed for specific use cases:
- Domestic payments: ACH, FPS, NPP, or DuitNow, depending on your location.
- Digital wallet transactions: Card network rails connected to Visa, Mastercard, or other global cards are typically the best option.
- Regular euro payments: SEPA is optimal.
- Large or non-Euro cross-border transactions: SWIFT or emerging fintech rails offer global reach and fast transfer speeds.
How to Choose the Right Payment Rail
When you’re selecting a payment rail, here are some things you should consider:
- Geographical Needs: International businesses may need SWIFT or SEPA, while US payroll could rely on ACH.
- Currency Support: Which currency are you trying to send? The Euro is best used with SEPA, while SWIFT supports a wide range of major currencies.
- Transaction Speed: Is speed more important than cost? For urgent payments, real-time or crypto rails might be preferable.
- Cost: ACH and SEPA are low-cost, while SWIFT and card payments tend to be higher.
- Business Scale: SMEs may prefer cost-effective digital solutions, while large enterprises may rely on SWIFT for global coverage.
Whichever rail you choose, ensure it is capable of getting your funds to your desired location with as little to no delay or charges on your or your recipients’ sides as possible.
Why Access to Multiple Payment Rails Matters
Relying on a single rail limits your flexibility. By accessing multiple payment rails, businesses and individuals can optimise for speed, cost, and reliability depending on the transaction. Using multiple rails offers:
- Resilience: If one rail is down or slow, payments can seamlessly route through alternatives without disrupting business operations.
- Cost Savings: Multiple rails let you choose the most affordable option for each transaction, for example, using SEPA for euro transfers instead of SWIFT.
- Global Reach: Combining local rails with global networks lets you pay and get paid easily anywhere.
- Scalability: Multi-rail strategies support both high-volume domestic transfers (e.g., ACH or NPP) and complex international payments (e.g., CHIPS or SWIFT).
In today’s interconnected economy, the ability to access and switch between multiple payment rails is not just convenient; it’s a competitive advantage.
How Multi-Rail Payment Strategies Work
Modern businesses use dynamic routing and payment APIs to decide which rails best serve each payment in real time.
For example, a company might route a payroll payment through ACH but send an international supplier payment via SWIFT or a fintech-enabled rail that offers faster settlements and lower fees.
Payment service providers often simplify multi-rail access by integrating dozens of rails into their systems. This lets their users perform cross-border transactions without having to manage their relationships with each rail provider.
In simple terms, individuals and businesses should use a service provider that is integrated with multiple rail networks to make their international transactions.
Final Thoughts
Payment rails form the backbone of today’s financial system. Some are built for local efficiency, others for international reach; each has its own strengths in speed, cost, and coverage.
The future of payments is multi-rail. Instead of relying on a single system, businesses and individuals are combining different rails to balance speed, cost, and compliance. This flexibility ensures that money can move quickly and reliably across borders and currencies.
FAQs about Payment Rails
Q: What are payment rails?
They are the systems and networks that enable money transfers between banks, businesses, and individuals.
Q: Which payment rail is faster?
Real-time rails like FPS (UK), SEPA Instant (EU) , NPP (Australia), and DuitNow (Malaysia) typically provide near-instant transfers. Some blockchain networks and stablecoin rails can also settle in real time, depending on adoption and network congestion.
Q: Are payment rails secure?
Yes, but security depends on the network. Established rails like SWIFT, CHIPS, and ACH follow strict compliance and security standards. Real-time rails (FPS, SEPA Instant, UPI) are also regulated by central banks. Digital wallets and online money transfer services are licensed by local regulators. Crypto/blockchain rails rely on decentralised security but may lack the same regulatory safeguards.
Q: Can businesses use multiple payment rails?
Yes, many businesses combine different rails to balance cost, speed, and coverage.
Q: What makes DSGPay stand out?
DSGPay is capable of connecting individuals and businesses to multiple rails under one platform with lower costs, a faster settlement time, lower FX costs, and seamless access to over 30 currencies.
DSGPay: The Best Multi-Rail Payment Provider For You
DSGPay connects individuals, SMEs, and large enterprises to multiple payment rails under one platform.
Whether it’s collecting funds through local systems like ACH, FPS, NPP, or DuitNow, or sending money internationally via SWIFT, DSGPay ensures every transaction takes the most efficient route.
Why DSGPay?
- Local and Global Named Accounts: Build trust with accounts in your business name for easy payments.
- Access Multi-Currency Accounts: Send, hold, convert, or receive payments in over 30 major currencies, all from a single dashboard.
- Transparent and Competitive Rates: DSGPay completes each transaction with the most competitive FX rates and transparent prices, providing a cost-effective solution to high transaction transfers.
- Access to Multiple Domestic and Global Rails: DSGPay has access to SWIFT, SEPA, ACH, and other domestic and global payment rails to rapidly settle payments.
- Seamless Integration: Connect easily with a single API for businesses and SMEs.
- Fully Licensed and Secure: DSGPay operates under a Hong Kong MSO licence. Strong AML standards support them, and they incorporate the latest security measures to safeguard every transaction from inception to completion.
With DSGPay, businesses gain the flexibility of multi-rail access, combining speed, cost savings, and security in one reliable platform.