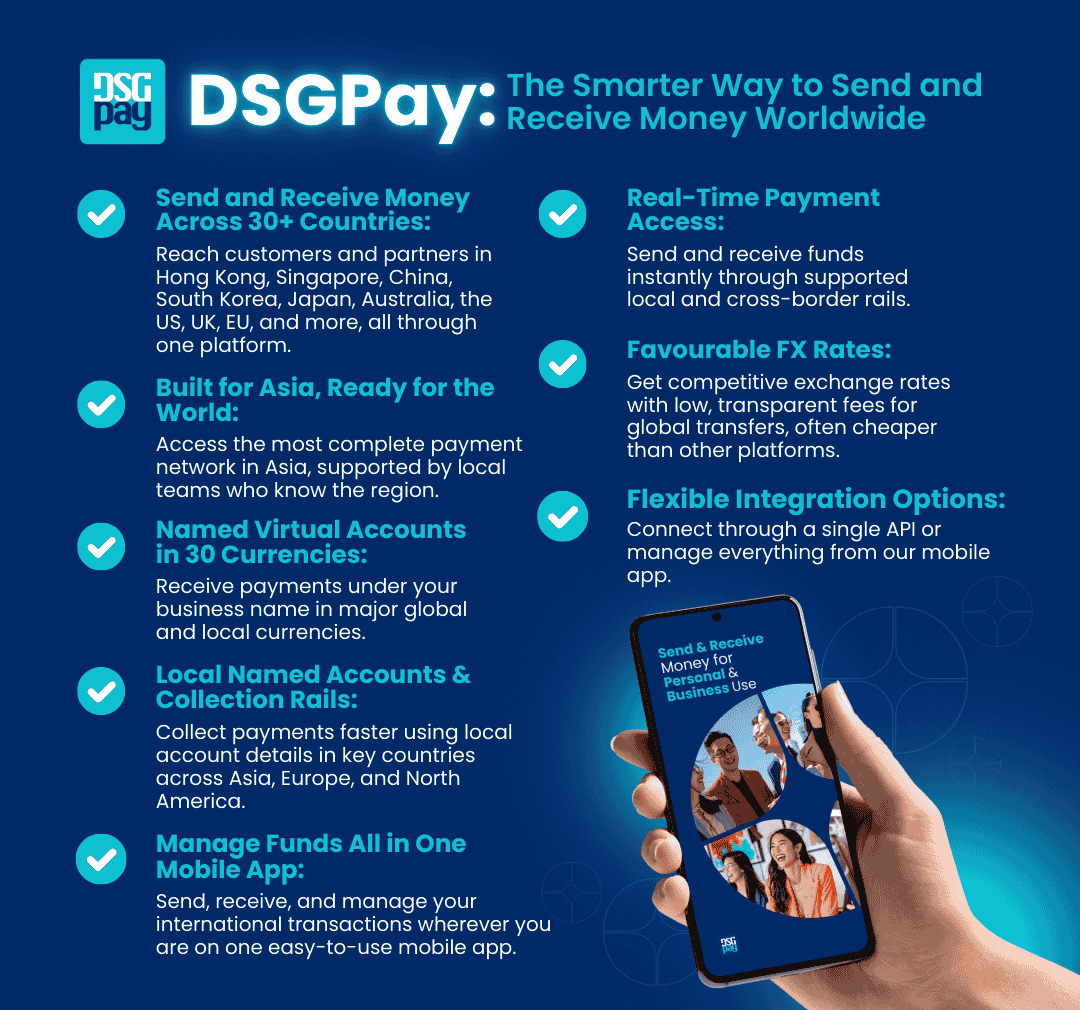
As the digital revolution transforms the financial industry, open banking is at the forefront, reshaping how financial services operate and innovate. This article introduces essential open banking definitions to help you understand this evolving landscape, unlocking new possibilities for financial management.
What Is Open Banking?
Open banking is a system where banks and financial institutions share customer data securely with authorized third-party providers (TPPs), provided they have the user’s consent. This data sharing is enabled through application programming interfaces (APIs) and fosters competition and innovation by allowing TPPs to provide services ranging from payment facilitation to financial management.
Understanding Essential Terms in Open Banking
As open banking reshapes financial services, it brings a new level of accessibility and personalization to the industry. Understanding the core terms of open banking is key to grasping how this system works and the value it offers.
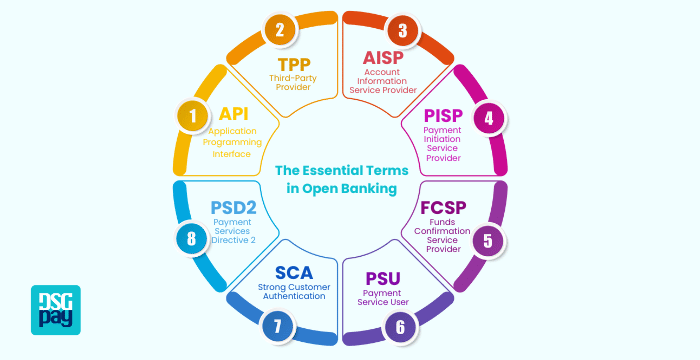
• API (Application Programming Interface)
APIs are central to the concept of open banking. Within open banking definitions, APIs are described as secure communication bridges that allow different software applications to exchange data efficiently. APIs enable authorized TPPs to access specific customer data from financial institutions with the customer’s permission. This seamless data exchange is foundational to open banking and is what makes customized financial solutions possible.
• TPP (Third-Party Provider)
Understanding open banking definitions also involves knowing what TPPs are. TPPs are external entities that offer financial services using data shared by banks through open banking APIs. These providers can offer various solutions, such as account aggregation, payment initiation, or financial management tools. By analyzing data from multiple accounts, TPPs help users make informed financial decisions.
• AISP (Account Information Service Provider)
AISPs are a specific type of TPP and are a key part of open banking definitions. AISPs focus on consolidating and displaying account information. By aggregating data from different bank accounts, AISPs provide users with a comprehensive view of their financial situation. For instance, an AISP could display account balances, transaction history, and other details across multiple banks, giving users a holistic view of their finances.
• PISP (Payment Initiation Service Provider)
Among open banking definitions, PISPs play a unique role as TPPs that initiate payments directly from a user’s bank account. PISPs create secure, seamless payment experiences by allowing users to initiate payments with their consent. This eliminates the need to switch between apps or re-enter payment details, streamlining the payment process and reducing transaction friction.
• FCSP (Funds Confirmation Service Provider)
Another term within essential open banking definitions is FCSP. FCSPs add an extra layer of assurance to transactions by confirming whether a user has sufficient funds for a specific transaction. This real-time fund verification supports smoother payment experiences, particularly in retail settings, where ensuring funds is crucial for uninterrupted transactions.
• PSU (Payment Service User)
PSUs refer to individuals or businesses that use payment services, often via TPPs. In open banking, PSUs are customers who grant permission for TPPs to access their financial data or initiate payments on their behalf. Understanding this term within open banking definitions highlights the user-centric nature of open banking, where control and consent are prioritized.
• SCA (Strong Customer Authentication)
One of the more security-focused open banking definitions is Strong Customer Authentication (SCA). Introduced under the Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2), SCA mandates additional identity verification steps for electronic transactions to enhance security. This ensures that only authorized users access sensitive data, reducing fraud risk. SCA typically involves multiple steps, like passwords, a one-time password (OTP), or biometrics, to secure online payments and data sharing.

• PSD2 (Payment Services Directive 2)
PSD2 is another critical concept among open banking definitions. As an EU directive, PSD2 is the regulatory framework enabling open banking by requiring data sharing between banks and authorized TPPs. This directive aims to create a competitive, innovative financial environment by granting secure access to data while maintaining strict security standards. PSD2 broadens the range of financial services and choices available to consumers.
Conclusion
Understanding these terms is key to unlocking the language and potential of open banking. As open banking continues to evolve, it will become an increasingly integral part of the global financial ecosystem.
To learn more about how open banking can revolutionise your financial services, contact DSGPay, your trusted partner in navigating the digital transformation of finance.