If you’ve ever gone through the process of sending money abroad, you must have come across the terms IBAN and SWIFT. And you must’ve thought, are they both the same? Well, the answer is no; both are completely different and used for different purposes when it comes to international transfers.
Let’s take a closer look at the IBAN vs. SWIFT difference and how they’re used to make sure your money reaches the right place.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- IBAN identifies the specific account, while SWIFT identifies the receiving bank.
- Most international transfers require both to ensure money is routed correctly and reaches the right account.
- They make cross-border payments faster, safer, and more reliable.
- New updates in 2025 improve security, speed, and fraud prevention.
IBAN vs. SWIFT: Key Differences Explained
| Feature | IBAN | SWIFT |
| Purpose | Identifies individual bank account | Identifies bank or branch |
| Format | Up to 34 alphanumeric characters (country-specific structure) | 8–11 alphanumeric characters |
| Usage | Mainly Europe, the Middle East, some other regions | Global (200+ countries) |
| Includes | Country code, check digits, bank code, account number | Bank code, country code, location, branch |
| Required For | Sending to a specific account | Routing payment between banks |
What is IBAN
IBAN stands for International Bank Account Number, and it works like a unique ID for your bank account when sending or receiving money from another country.
Before IBAN, every country had its own account number format, which often led to mistakes; payments got delayed, ended up in the wrong place, or were rejected altogether.
IBAN solved this by creating a clear, standard format that banks around the world can understand. It makes international transfers faster, safer, and more accurate.
How IBAN Works
- You enter the recipient’s IBAN when making an international payment.
- The sending bank checks the IBAN’s format and verifies the check digits for accuracy.
- The IBAN identifies the correct country and bank where the account is held.
- The payment is routed through the banking network to the recipient’s bank.
- The bank uses the IBAN to locate the exact account.
- The money is deposited into the correct account.
IBAN Format and Structure
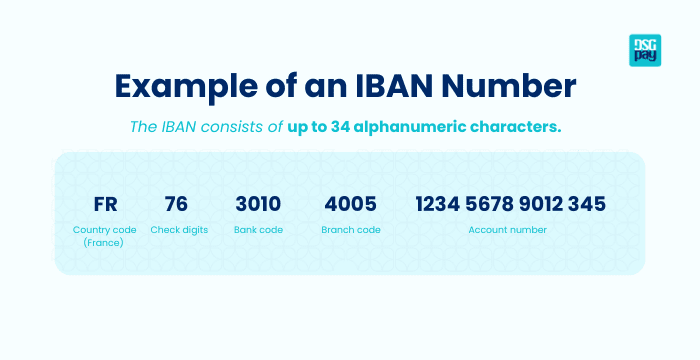
An IBAN is built using a specific format that gives banks all the information they need:
- Country code (2 letters): Show where the account is based
- Check digits (2 numbers): Verify the code is valid
- Account details: A mix of letters and numbers that identify the bank and the specific account
Where IBAN is Required
Many countries now require an IBAN for international transfers. In some places, you also need it for local bank transfers, while others simply recommend using it.
- Required for both international and local payments: Most of Europe and the Middle East, including France, Germany, Italy, Spain, the UAE, and Turkey.
- Required only for international payments: Countries like Denmark, Poland, Saudi Arabia, Norway, and Serbia.
- Recommended but not mandatory: The UK, Brazil, Pakistan, and a few others.
Some territories follow their parent country’s rules. For example, French overseas regions use France’s IBAN system, and the Isle of Man follows the UK’s rules. It’s always best to check with your bank before sending a transfer, as requirements can vary.
Why IBAN is Important
- It reduces errors and failed payments.
- It speeds up international transfers by providing clear account details.
- It helps banks verify transactions before sending money.
Now let’s look at how the SWIFT structure is organised.
What is SWIFT
SWIFT, which stands for Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (also known as a BIC), is a global network that banks and financial institutions use to send secure payment instructions across borders.
While IBAN identifies the specific account, SWIFT identifies the receiving bank. It doesn’t move the money itself but enables banks to complete transfers through their own systems.
How SWIFT Works
Here’s how the process usually happens:
- When you make an international payment, your bank creates a secure message with all the transaction details, including the amount, currency, and recipient’s information.
- This message is sent through the SWIFT network to the recipient’s bank, identified by its unique SWIFT code.
- If the two banks don’t have a direct connection, intermediary (correspondent) banks help pass the message along.
- The actual money moves between banks through nostro accounts (your bank’s account held in a foreign bank) and vostro accounts (a foreign bank’s account held in your bank).
- Once the recipient’s bank receives the message, it processes the payment and credits the money to the correct account.
SWIFT Code Format
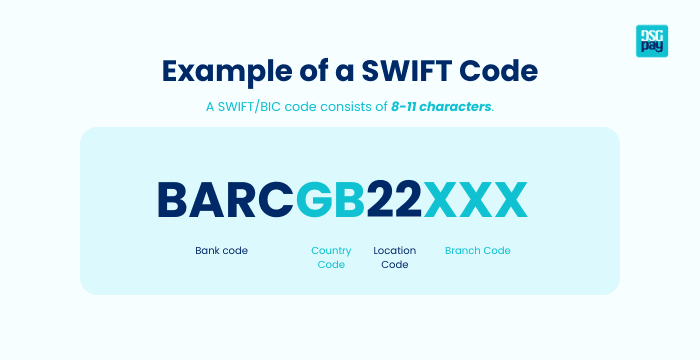
Every bank that uses SWIFT has a unique code, often called a BIC (Bank Identifier Code). It’s usually 8 to 11 characters long and follows a simple format:
- Bank code (4 letters): Identifies the bank.
- Country code (2 letters): Shows which country the bank is in.
- Location code (2 letters or numbers): Tells you the bank’s city or region.
- Branch code (3 optional characters): Points to a specific branch if needed.
Where SWIFT is Used
You need a SWIFT or BIC code for most international transfers. It’s essential when sending money to countries that do not use IBANs, like the United States, Canada, and Australia. It’s also required for payments to many countries within the Eurozone, such as Germany, France, and Italy, to make sure the money reaches the correct bank.
Why SWIFT is Important
- SWIFT is used by over 11,500 financial institutions in more than 200 countries.
- It allows money to move quickly, securely, and accurately around the world.
- More than 53 million messages are sent through the network every day.
- Most payments reach the recipient bank in under 10 minutes.
- The network is highly reliable, with 99.999% uptime.
- SWIFT also supports trading, securities, and business transactions and is preparing to handle digital currencies in the future.
How IBAN and SWIFT Work Together
While IBAN and SWIFT are two separate systems, they are often used together in the same international transfer to make sure payments reach the correct account safely and securely.
When you send money abroad:
- The SWIFT network securely transmits the payment message between banks across different countries.
- The IBAN within that message specifies the exact recipient account at the destination bank.
In short, SWIFT handles the communication, and IBAN provides the account details.
How to Find Your IBAN and SWIFT Code
Finding these codes is easy. Here’s how:
- Bank statements: Most banks list them on your printed or digital statements.
- Online banking: You can usually find them under account details.
- Mobile apps: Many banking apps display them clearly on the account page.
- Contact your bank: If you’re unsure, your bank’s support team can confirm them.
Before you send money, make sure every digit is correct. A small mistake can cause long delays or extra fees.
IBAN and SWIFT in 2025: Smarter, Safer, and More Reliable
International payments are becoming more advanced, and IBAN and SWIFT remain central to the process. In 2025, major upgrades are focused on improving speed, accuracy, and security.
- More options: Fintech platforms are providing cheaper alternatives for cross-border payments, but SWIFT continues to be the most widely used system.
- Real-time checks: Banks now verify IBAN details before processing payments, reducing errors and preventing failed transfers.
- Stronger compliance: SWIFT is tightening security by enforcing sanctions and blocking certain banks to protect the global payment network.
- Clearer formats: IBANs are becoming more standardised and easier to read, helping payments move more smoothly between banks.
- Better messaging: The new ISO 20022 format improves payment data, making transfers faster and easier to track.
- Global fraud protection: Confirmation of Payee is being rolled out worldwide, allowing senders to check account names and details before sending money.
For individuals and businesses, these improvements mean faster payments, fewer errors, stronger security, and better visibility across borders.
Final Thoughts
IBAN and SWIFT might look complicated at first, but once you understand what they do, it’s simple. IBAN identifies the specific account where the money should go, while SWIFT ensures it’s sent through the right bank.
For most international transfers, you’ll need both. Get them right, and your money will arrive quickly and safely.
Making Your Global Transfer Easier with DSGPay
Understanding how IBAN and SWIFT work is only the first step; managing them across different countries, currencies, and banking systems is the real challenge.
With DSGPay, individuals and businesses can simplify international payments through local payment rails and named virtual accounts that function like local bank accounts in key markets, all managed through a single platform.
Why choose DSGPay for international transfers?
- Global Access: Send, hold, and receive funds in 30+ currencies through multi-rail networks, including SWIFT, SEPA, and ACH.
- Named Virtual Accounts: Receive payments under your business name, building trust and ensuring accuracy for clients worldwide.
- Real-Time Settlement: Enjoy faster payouts and collections with local rails in major markets such as Hong Kong, the UK, Europe, and Australia.
- Competitive FX Rates: Convert currencies at transparent, real-time rates, and no hidden fees.
- Secure and Compliant: Operating under a Hong Kong MSO license, DSGPay meets stringent global compliance and AML standards.
Whether you’re paying suppliers, managing global payouts, or receiving payments from clients abroad, DSGPay takes the complexity out of IBAN vs. SWIFT transfers. We help you focus on growing your business while handling the heavy lifting of international payments behind the scenes.